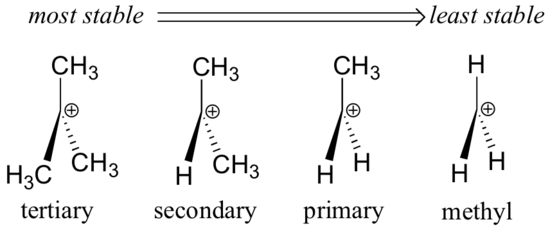
That means that tertiary is more stable than secondary secondary more stable than primary and primary more stable than methyl.
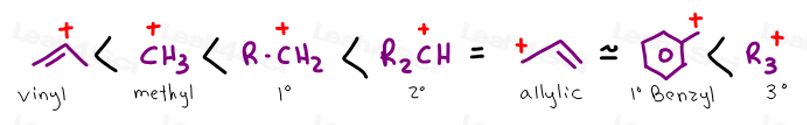
Which is more stable vinyl carbocation or a primary carbocation.
Vinyl cations are located on sp hybridized carbons.
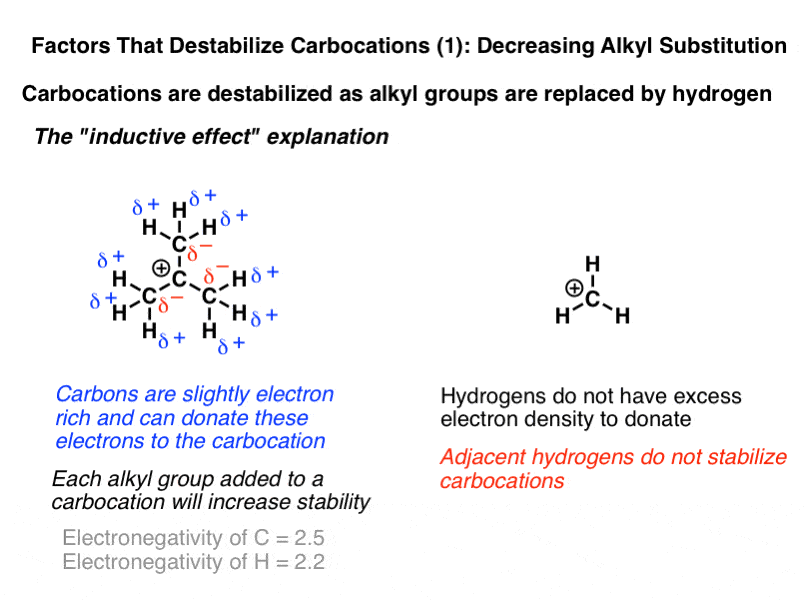
The more r groups a carbocation has attached the more stable it is.
But carbocation 5 is vinylic carbocation positively charged carbon is sp 2 hybridized i.
It is possible to demonstrate in the laboratory see section 16 1d that carbocation a below is more stable than carbocation b even though a is a primary carbocation and b is secondary.
Primary phenyl vinyl methyl allyl benzyl methoxymethyl most stable least stable important note.
The vinyl cations are less stable due to the difference in hybridization of the carbon bearing the positive charge.
The hybridization of a vinyl carbocation is sp hybirdized.
One way of determining carbocation stabilities is to measure the amount of energy to form the carbocation by dissociation of the corresponding alkyl halide while the tertiary alkyl halide dissociates to give carbocations more easily than secondary or primary ones which result in tri substituted carbocations are found to be more stable than di substituted and in turn are more stable than mono substituted.
Although primary resonance stabilized carbocations allyl cation benzyl cation and methoxymethyl cation are less stable than tertiary carbocations secondary resonance stabilized carbocations more stable than tertiary carbocations.
The most stable version is the tertiary benzylic carbocation.
We have one more case in this example with primary carbocations 1 and 5.
Carbon with two other atoms attached prefers sp hybridization and a linear geometry.
The carbocation 1 is a saturated carbocation which is stabilized by hyperconjugation.
As you increase substitution the benzylic carbocation becomes more and more stable.
The difference in stability can be explained by considering the electron withdrawing inductive effect of the ester carbonyl.
In general you probably won t see a primary or methyl carbocation in o chem 1.
Compound i is more stable among all as it is a tertiary carbocation then comes compound ii which is a secondary carbocation compound iv is a primary carbocation compound ii is a secondary carbocation with an electron withdrawing group close to it which makes it unstable.